Doctor’s Note: Your Essential Guide to Rosacea and More
As dermatologists, we understand that dealing with rosacea can be challenging. The redness can often flare up unpredictably, leading to frustration and a lack of control. There are a lot of treatment options, and we’ve tried to clarify options for you.
Watch the video summary to the right, or read on for more!
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a long-term condition that mainly affects the skin on the face, causing redness and sometimes small, visible blood vessels. For some, it can also lead to red bumps that may look like acne. Rosacea tends to flare up in cycles, with periods where symptoms worsen and other times when they calm down. While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, factors like genetics, immune system response, and environmental triggers play a role.
Rosacea Subtypes
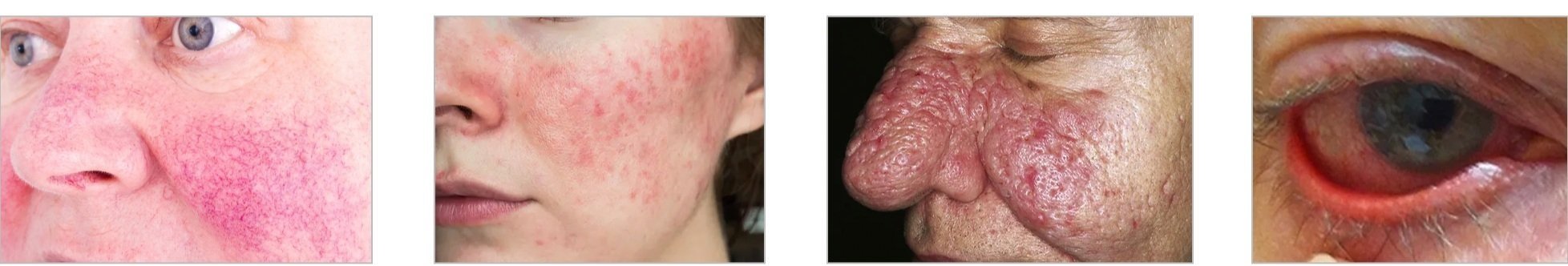
Rosacea is not one-size-fits-all; it comes in four main subtypes, each with distinct symptoms.
1. Flat, Red Rosacea
This subtype is marked by persistent redness and visible blood vessels, particularly on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. Flushing, or sudden episodes of intense redness, is also common.
2. Acne Rosacea
Often confused with acne, this type of rosacea involves red bumps (papules) and pus-filled blemishes (pustules). It’s often seen in middle-aged women.
3. “Large Nose” Rosacea
This subtype thickens the skin, most commonly around the nose, but it can also affect the chin, forehead, cheeks, or ears. The thickened skin may become bumpy.
4. Eye Rosacea
This form affects the eyes, causing redness, irritation, dryness, and sensitivity to light. The eyelids can become swollen, and in severe cases, vision may be affected.
While there are four subtypes of rosacea, Subtypes 1 & 2 are the most common. Here, we will focus on these two subtypes.
What Causes Rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea is unknown, but several factors are believed to play a role:
Genetics: Rosacea tends to run in families.
Immune system: Some people with rosacea have a skin reaction involving the immune system.
Environmental factors: Sun exposure, extreme temperatures, wind, and hot baths can trigger rosacea.
Mites: A mite that normally lives on human skin (Demodex folliculorum) may be more abundant in people with rosacea.
What Makes Rosacea Better?
Sun protection: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, as sun exposure is a common trigger.
Gentle skincare: Choose mild, non-irritating cleansers and moisturizers to avoid further irritation.
Healthy diet: Avoid trigger foods and drinks like spicy foods, alcohol, and hot beverages.
Stress management: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to reduce stress.
Stay cool: Avoid hot showers, saunas, or hot tubs, as heat can trigger flare-ups.
Moisturize regularly: Use a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep skin hydrated and protect the skin barrier.
Avoid rubbing or scrubbing: Be gentle with your skin, as rubbing can worsen redness.
Anti-redness products: Consider over-the-counter products with soothing ingredients like niacinamide or licorice extract.
Consult a dermatologist: Work with a specialist to find the right treatment plan, including prescription creams, oral medications, or procedures like lasers.
What Makes Rosacea Worse?
Avoiding known triggers is essential for managing rosacea, as it can help minimize flare-ups and control symptoms. Keeping a daily diary to monitor activities, foods, and environmental factors can help identify personal triggers and effectively manage the condition. Here is a brief overview of common triggers:
Food: Alcohol, Spicy food, Chocolate, Coffee, Caffeine, Certain dairy, meats, fruits, vegetables
Heat: Sunlight, Hot weather, Hot drinks, Hot showers, Indoor heat, Exercise, Saunas
Weather: Sunlight, Temperature Changes, Wind, Cold, Humidity
Skin: Irritating substances, Microbial changes, Skin barrier disruption, Certain skincare products, Certain cosmetics
General: Stress, Embarrassment, Medications, Medical conditions
Often, rosacea patients find it difficult to pinpoint their exact trigger. If you don't know what is flaring you, it's important to keep a daily journal to record the day's foods/stressors/events so you can look back and find your triggers. Download a daily printable journal below!
Step-by-Step Instructions to Manage Rosacea Flare
Cleanse Gently: Wash your face with a mild, non-irritating cleanser. Don’t scrub or use hot water.
Apply a Cool Compress: Place a cool, damp cloth on your face for 5-10 minutes to calm irritation and reduce redness.
Use Anti-Redness Products: Apply a prescribed topical treatment, like metronidazole or prescription Rhofade, to lower redness and swelling.
Moisturize: Use a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated and help repair the skin barrier.
Avoid Triggers: Stay away from triggers like spicy foods, alcohol, and extreme temperatures that can worsen symptoms.
Protect Your Skin: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher to prevent sun-induced flare-ups.
Monitor Symptoms: Track your symptoms and note any patterns or triggers. Adjust your skincare routine and lifestyle as needed.
Consult Your Dermatologist: If your flare-up doesn’t improve or gets worse, contact your dermatologist for further advice and possible treatment changes.
Best Products for Rosacea
Rosacea = sensitive skin. You must treat rosacea-prone skin VERY gently with fragrance-free products. Remember, what works for someone else may not work for you. You may have to buy a few well-reviewed gentle cleansers, moisturizers, and sunscreens, trial each one, and return what doesn't work for you. Check out a few of our favorite gentle skincare products below.
Best Face Wash for Rosacea
Choose only gentle, fragrance-free cleansers. Favorite brands include Aveeno, Cetaphil, Cerave, and Vanicream. Cleanse 1 - 2x per day (a cleanse can be simply splashing your face with water). Your face should not feel “squeaky clean” after a cleanse!
Best Moisturizer for Rosacea
Opt for mild, fragrance-free moisturizers to keep your skin hydrated and calm. Recommended brands like Aveeno, Cetaphil, Cerave, and Vanicream can be used 1-2 times daily.
Best Skincare for Rosacea
There are topicals that can reduce inflammation. Arnica, azelaic acid, sulfur, and hypochlorous acid.
Best Sunscreen for Rosacea
Look for mineral sunscreens (contain zinc oxide or titanium dioxide), as these are more gentle on very sensitive skin. Sunscreen daily is a must for people with rosacea!
In addition to the above skincare tips, rosacea can also be managed with prescriptions and procedures.
Rosacea Treatment Overview
To treat rosacea, doctors usually start with gentle skincare routines and over-the-counter products to reduce redness. Prescription creams and gels can also help lower inflammation. For more severe symptoms, doctors may prescribe oral antibiotics. Laser therapy is another option to reduce redness and visible veins. It’s also important to avoid triggers like spicy foods, alcohol, and extreme temperatures, as these can make rosacea worse. Always talk to your dermatologist to find the best treatment plan for you.
Best Topical Prescriptions for Rosacea
These are creams, gels, and lotions applied directly to the skin to reduce redness and inflammation. Here is a brief overview of some of the prescription treatments available:
Rhofade: Rhofade is a daily cream that temporarily tightens blood vessels to reduce redness. While effective, it may cause side effects like worsening redness after the cream wears off (“rebound erythema”), as well as itching and burning.
Best For: Flat, Red Rosacea (Subtype 1)
Mirvaso: Mirvaso is a daily gel that works by temporarily constricting blood vessels to reduce redness. However, it can cause side effects like worsening redness after the gel wears off (“rebound erythema”), along with itching and burning.
Best For: Flat, Red Rosacea (Subtype 1)
Soolantra contains ivermectin and is used to treat rosacea. It kills tiny mites called Demodex, which may play a role in rosacea. It also helps reduce inflammation.
Best For: Mild Acne Rosacea (Subtype 2)
Finacea contains azelaic acid and is used to reduce bumps caused by rosacea.
Best For: Mild Acne Rosacea (Subtype 2)
Antibiotics used for treating rosacea include metronidazole, clindamycin, and erythromycin.
Best For: Mild Acne Rosacea (Subtype 2)
Elidel is a non-steroidal treatment that reduces inflammation and is safe for daily use. (Remember, we can’t use steroids on rosacea!)
Best For: Mild Acne Rosacea (Subtype 2)
Sulfur is available in washes, creams, and lotions. It has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, making it useful for treating rosacea.
Best For: Mild Acne Rosacea (Subtype 2)
Best Oral Prescriptions for Rosacea
Oral medications are often prescribed for moderate to severe cases of rosacea, especially when there are bumps and pimples.
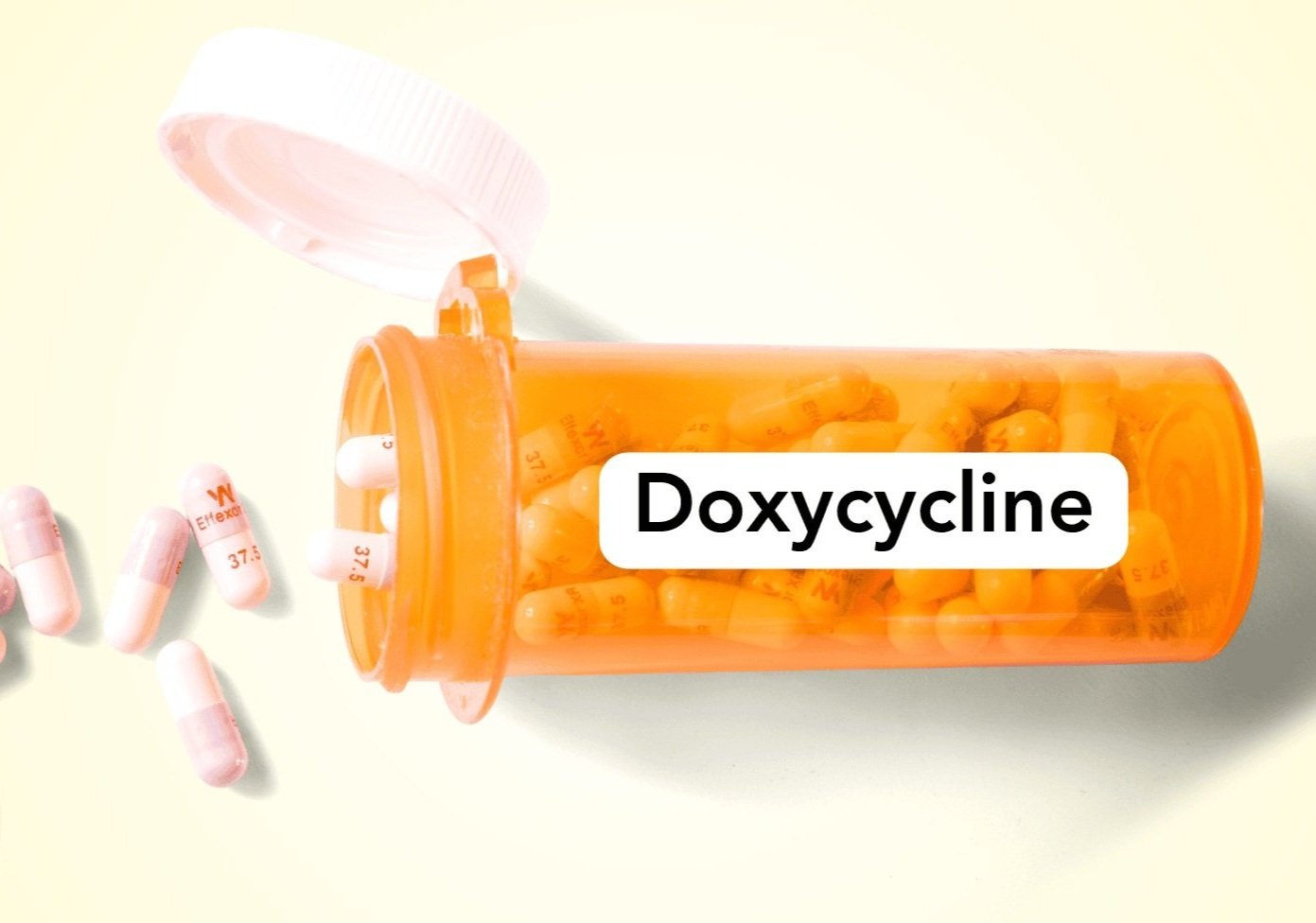
Doxycycline is a generic antibiotic commonly used for its anti-inflammatory effects, even though rosacea isn’t caused by bacteria. Patients with rosacea usually take a low daily dose to help manage symptoms. However, it can sometimes cause stomach upset.
Best For: Severe Acne Rosacea (Type 2)
Oracea is a brand name for a low-dose doxycycline (40mg). The dose is so low that it’s not considered an antibiotic but rather an anti-inflammatory treatment for rosacea. It's also less likely to cause stomach upset compared to higher doses.
Best For: Severe Acne Rosacea (Type 2)
Accutane, or isotretinoin, is a strong medication for severe acne and rosacea. It works by reducing oil production, but it comes with side effects. The most common are dryness of the skin, lips, and eyes.
Best For: Severe Acne Rosacea (Type 2)
Oh boy, those are a lot of options. Which one is for me?
Whenever a condition has a lot of treatment options, it means none of them work particularly well, and it's a bit of trial-and-error to find what works for your unique skin. Typically, we start with either Soolantra or Finacea, but sometimes, treatment is limited by insurance coverage. 🫠
Best Procedures for Rosacea
While skincare is important, some people need more advanced treatments to manage their rosacea. Here are a few of the most effective options:
Microneedling for Rosacea
Microneedling uses tiny needles to create small injuries in the skin, boosting collagen production. It may help reduce redness and improve skin texture in some people with rosacea. Consult a dermatologist to ensure it's safe for your skin type.
Botox for Rosacea
While Botox is known for treating wrinkles, some studies suggest it can also reduce redness and flushing in rosacea by relaxing facial blood vessels. More research is needed, but it may be helpful for managing severe rosacea symptoms.
V Beam for Rosacea
The V Beam laser targets blood vessels to reduce redness and visible veins, making it a popular choice for moderate to severe rosacea. It can improve the skin’s overall appearance.
BBL for Rosacea
BroadBand Light (BBL) therapy uses light energy to treat redness and visible veins. It’s a non-invasive option that can improve rosacea, especially for those with persistent redness.

How to Get Rid of Rosacea Permanently
Unfortunately, there is no permanent cure for rosacea. However, with the right combination of treatments, skincare, and lifestyle changes, you can manage your symptoms and keep flare-ups to a minimum. Working with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan is the best way to get long-term relief from rosacea symptoms.
Rosacea FAQs
Does microneedling help rosacea?
Microneedling is generally not recommended for rosacea, as it can exacerbate redness and sensitivity. However, some specialized treatments may be suitable for certain types of rosacea when performed by a dermatologist.
Does vitamin C help rosacea?
Vitamin C can help reduce redness and inflammation associated with rosacea if used in a gentle, low-concentration formula. Avoid formulations that are too acidic, as they can irritate sensitive skin.
Is retinol bad for rosacea?
Retinol can irritate rosacea-prone skin, potentially worsening symptoms. If used, start with a low concentration and consult a dermatologist for advice on incorporating it into your routine.
Does Accutane help rosacea?
Accutane (isotretinoin) may help severe cases of rosacea, especially those with acne-like symptoms, but it is typically used as a last resort under close medical supervision.
Does aloe vera help rosacea?
Aloe vera can soothe irritation and reduce redness in rosacea-prone skin, provided it is pure and free of added fragrances or alcohol.
Is rosacea autoimmune?
While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, it is not classified as an autoimmune disease. It is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
What kind of facial soap to use for rosacea?
Gentle, fragrance-free, and non-comedogenic facial cleansers are best for rosacea. Look for cleansers labeled as suitable for sensitive skin.
How to calm a rosacea flare-up fast?
To calm a rosacea flare-up, avoid triggers such as heat or alcohol, apply a cold compress, use soothing moisturizers, and consider over-the-counter anti-inflammatory products like niacinamide.
How long to take doxycycline for rosacea?
Doxycycline is typically prescribed for rosacea for 6-12 weeks, but the duration may vary based on individual response and severity. Always follow your doctor's instructions.
How to get rid of rosacea permanently?
There is no permanent cure for rosacea. However, it can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes, proper skincare, and medical treatments like topical medications, oral antibiotics, or laser therapy.
Is metronidazole cream or gel better for rosacea?
Both cream and gel forms of metronidazole are effective for rosacea, but gels are often preferred for oily skin, while creams may suit dry or sensitive skin better.
Can skincare products trigger rosacea?
Yes, certain skincare products containing fragrances, alcohol, or harsh chemicals can trigger or worsen rosacea. Always choose products formulated for sensitive skin.
Does rosacea itch?
Rosacea can cause itching in some cases, particularly if the skin is dry, inflamed, or irritated by triggers.
Can you have 2 types of rosacea?
Yes, it is possible to have more than one type of rosacea simultaneously, such as erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (redness) and papulopustular rosacea (acne-like bumps).
Is rosacea genetic?
Yes, rosacea often runs in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. However, environmental and lifestyle factors also play a significant role.